High-protein diets have become a cornerstone of modern health and fitness culture. Promising weight loss, muscle development, and increased energy, this trend has swept across gym-goers, office workers, and even casual dieters. But as protein becomes the centerpiece of countless diets and food marketing campaigns, many wonder if we’ve gone too far. Are these diets truly as beneficial as they seem, or are we prioritizing protein over balance?
The Origins of the Protein Obsession
Protein’s nutritional importance isn’t new, but its rise as a dietary superstar began decades ago. Programs like Atkins and South Beach paved the way for low-carb, high-protein eating plans, and more recently, Keto and Paleo diets have reignited the protein craze. Social media has played a key role in promoting these diets, with influencers sharing protein-packed recipes and tips.
Meanwhile, research-backed claims about protein’s role in weight loss, satiety, and muscle building have bolstered its popularity. But is this a case of science meeting marketing in a way that prioritizes profit over health?
The Science Behind Protein
Protein is one of the three macronutrients essential for life, along with carbohydrates and fats. It plays a critical role in:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Protein aids in repairing tissues, especially after exercise.
- Hormonal and Enzymatic Functions: Many hormones and enzymes are made up of proteins.
- Immune Support: Proteins support antibody production to fight off infections.
Despite its necessity, the overemphasis on protein often leads people to ignore other crucial dietary needs.
Why Are High-Protein Diets So Popular?
Weight Management Benefits
Protein helps control hunger by increasing satiety. Dieters often find it easier to stick to calorie limits when meals are protein-heavy.
Fitness Enthusiasts’ Ally
Athletes rely on protein to rebuild muscles after workouts. Many believe high-protein diets accelerate fitness progress.
The Appeal of Simplicity
Protein diets often reduce complex meal planning, focusing on simple, protein-dominant meals. This simplicity makes them easy to follow.
The Hidden Dangers of Protein Overload
Digestive Troubles
Excessive protein intake can lead to dehydration and gastrointestinal discomfort due to the strain on the kidneys.
Dietary Imbalance
Focusing too much on protein can crowd out other essential nutrients like fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
Potential Long-Term Health Risks
Diets heavy in red and processed meats may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues and certain cancers.
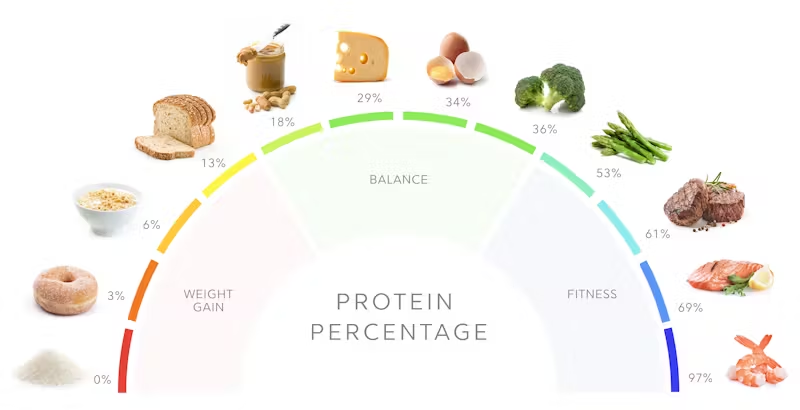
Not All Protein Is Created Equal
Protein sources vary greatly in quality and health impact.
- Best Choices: Lean meats, eggs, fish, legumes, and tofu.
- Moderate: Dairy products and plant-based protein powders.
- Limit: Red meats and processed protein products like sausages and bacon.
Plant-based proteins like lentils and chickpeas offer additional benefits, including fiber and reduced environmental impact.
Protein Beyond Meat: The Plant-Based Boom
As concerns about sustainability and health rise, plant-based protein options are gaining popularity. Foods like tempeh, quinoa, and pea protein powders are viable alternatives to animal proteins, offering similar nutritional benefits with a smaller environmental footprint.
The Role of Marketing in the Protein Boom
Protein-enriched snacks, shakes, and cereals are flooding the market. While convenient, these products often come with inflated prices and questionable health claims. Reading labels is crucial to avoid falling for marketing gimmicks.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
- General Guidelines: The average adult needs about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily.
- Specific Needs: Athletes or those recovering from illness may require more, around 1.2 to 2 grams per kilogram.
- Reality Check: Most people meet or exceed their protein needs without supplementation.
Common Misconceptions About Protein
Myth: More Protein Equals More Muscles
Reality: Muscle growth also requires adequate calorie intake, resistance training, and rest.
Myth: High-Protein Diets Work for Everyone
Reality: Individual needs vary, and what works for a bodybuilder may not suit a sedentary individual.
Environmental Concerns of the Protein Craze
Animal protein production, especially beef, has significant environmental costs. Reducing reliance on meat and choosing sustainable options like plant-based proteins can make diets healthier and more eco-friendly.
Tips for a Balanced Approach to Protein
- Include Variety: Combine animal and plant-based proteins for a well-rounded diet.
- Avoid Over-Reliance: Don’t let protein overshadow fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Read Labels: Be wary of protein-enriched products with unnecessary additives or high sugar content.
- Stay Hydrated: Increased protein intake requires proper hydration to prevent kidney strain.